BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension
BART Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.13461.pdf
BART Code: https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq/tree/main/examples/bart
BART is a transformers[1] based sequence to sequence model where it’s encoder is bidirectional like BERT[2] and decoder is auto-regressive like GPT[3].
BART Pretraining has two stages:
- Text is corrupted with an arbitrary noising function, and
- A sequence-to-sequence model is learned to reconstruct the original text.
This is the reason for calling BART is denoising autoencoder.
BART is particularly effective when fine tuned for text generation but also works well for comprehension tasks. It matches the performance of RoBERTa with comparable training resources on GLUE and SQuAD, achieves new stateof-the-art results on a range of abstractive dialogue, question answering, and summarization tasks, with gains of up to 6 ROUGE.
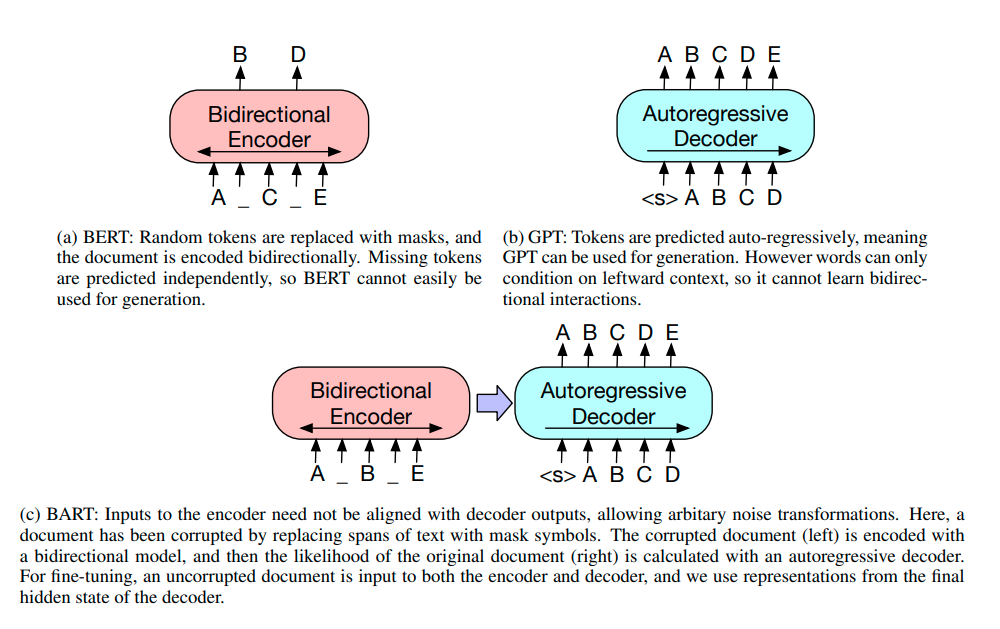
BART Architecture
- BART uses the standard sequence-to-sequence Transformer[1] architecture from (Vaswani et al., 2017)
- BART use GeLU activation function
- BART initialize parameters from N(0, 0.02)
- For base model it has 6 layers in the encoder and decoder
- For large model it has 12 layers in encoder and decoder
- BART didn’t use additional feed-forward network in top before word prediction like BERT
- BART contains 10% more parameters than BERT model
Pre-training
- BART is trained by corrupting documents and then optimizing a reconstruction loss—the cross-entropy between the decoder’s output and the original document.
- Unlike existing denoising autoencoders, which are tailored to specific noising schemes, BART allows us to apply any type of document corruption.
- There four types noising happens in BART pretraining.
- Token Masking
- Token Deletion
- Text Infilling
- Sentence Permutation
- Document Rotation
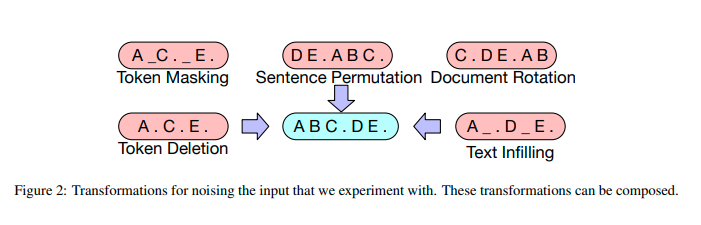
Noising Functions
- Token Masking: Random tokens are sampled and replaced with [MASK] elements.
- Token Deletion: Random tokens are deleted from the input. In contrast to token masking, the model must decide which positions are missing inputs.
- Text Infilling: A number of text spans are sampled, with span lengths drawn from a Poisson distribution (λ = 3). Each span is replaced with a single [MASK] token. 0-length spans correspond to the insertion of [MASK] tokens. Text infilling is inspired by
SpanBERT[4], but SpanBERT samples span lengths from a different (clamped geometric) distribution, and replaces each span with a sequence of [MASK] tokens of exactly the same length. Text infilling teaches the model to predict how many tokens are missing from a span. - Sentence Permutation: A document is divided into sentences based on full stops, and these sentences are shuffled in a random order.
- Document Rotation: A token is chosen uniformly at random, and the document is rotated so that it begins with that token. This task trains the model to identify the start of the document.

Comments